
|
SuperTeacherTools |
|

|

|
NEMO
Incontinential Pigmenti
Stages:
1 = Vesicular
2 = Verrucous
3 = Hyperpigmentation
4 = Hypopigmentation
400 - 410 nm
Ehlers-Danlos Type IV (Vascular Type)
Type 3 collagen abundant in skin, lungs and vasculature.
Thin, translucent, easily bruisable skin, thin nose and upper lip.
Joint mobility is normal, although atlantoaxial subluxation can occur.
Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia (Osler-Weber-Rendu)
Endoglin (ENG) or Activin receptor-like kinase-1 (ACK1, ACVRL1) -> proteins belonging to TGF-beta receptor complex that play a role in forming the vascular system
Telangiectasias, epistaxis, melena, AV malformations in liver, lung, CNS
Diabetic Dermopathy or "Shin Spots" or Pigmented Pretibial Papules
Bilateral asymptomatic red-brown atrophic macules on the shins
No effective treatment.
Diabetic Limited Joint Mobility = Cheiroarthropathy
Tightness and thickening of the skin and periarticular tissue of the fingers with resultant painless loss of joint mobility
Physical therapy and tight control of hyperglycemia
Werner Syndrome (Adult Progeria)
Growth arrest at puberty, premature aging/balding/graying, sclerodermoid appearance, poikiloderma, leg ulcers, painful callosities of feet and ankles, and cataracts by age 30
Premature cardiac atherosclerosis accounts for early death
Type 2 DM, tumors of uterus, breast, liver and thyroid.
XPD=ERCC2 or XPB=ERCC3 (DB = Dark Bands)
Trichothiodystrophy or PIBIDS or Tay's Syndrome
Photosensitivity, Ichthyosis, Brittle hair, Intellectual impairment, Decreased fertility, Short stature
Reduced sulfur content in hair
Polarosocpy reveals tiger tail banding or trichothiodystrophy. Can also see trichoschisis, pili torti, trichorrhexis nodosa.
Photosensitivity but no increased risk of skin cancer.
Necrobiosis Lipoidica Diabeticorum (NLD)
Thought to be secondary to nonenzymatic glycosylation of dermal collagen and elastin.
Ulcer prevention. No impact of tight glucose control on developing NLD, but diabetics with NLD have higher rate of microvascular complications and limited joint mobility.
Sjögren–Larsson syndrome
FALDH (Fatty aldehyde dehydrogenase) deficiency (they fall down) --> accumulated fatty alcohol/aldehyde lipids
More common in Sweden
Triad of congenital ichthyosis, di- or tetraplegia, mental retardation
Perifovial glistening white dots (fall down, see stars), grand mall seizures.
U R Totally Nailed After Last Night's Party, Dude...
UVA
Renal failure on HD
Tetracycline
Nalidixic acid (quinolone Abx)
Amiodarone
Lasix
Naproxen/NSAIDs
Pyridoxine
Dapsone
Kaposi's Sarcoma
Scleredema Diabeticorum
Type 1 = Acute type secondary to strep pyogenes
Type 2 = Associated paraproteinemia
Type 3 = Type 2 DM
Marfan's Syndrome
Striae distensae, abdominal wall hernias, elastosis perforans serpiginosa, upward ectopia lentis, tall stature, hyperextensible joints, pectus excavatum, arachnodactyly, kyphoscoliosis, emphysema, pneumothorax, Gorlin sign
VMCM1 gene - Blue Rubber Bleb Nevus Syndrome
Autosomal dominant or sporadic
Cutaneous lesions, GI lesions -> melena
Lung, eye and CNS lesions
aka Dermatitis Herpetiformis:
Anti-Gliadin
Anti-Tissue Transglutaminase or Anti-Epidermal Transglutaminase
Anti-Endomysial
HyperAndrogenism
Insulin Resistance
Acanthosis Nigricans
Homocystinuria
Deficient cystathionine beta synthase -> elevated srum homocysteine -> inhibition of collagen cross-linking
Arterial and venous thromboses, generalized osteoporosis, mental retardation, downward ectopia lentis.
Tx: Avoid methionine and homocysteine. Supplement with cysteine, pyridoxine, folate, B12.
Brack Syndrome
Arthrogryposis: ("Hooked or curved joints") Multiple joint contractures, muscle weakness, fibrosis
Cowden's Syndrome
Bannayan-Riley-Ruvalcaba
Proteus Syndrome
626 nm (diagnostic)
Neurofibrosarcoma
Malignant Peripheral Nerve Sheath Tumor
Erythropoietic Protoporphyria (EPP)
Ferrochelatase deficiency
Cockayne Syndrome
Genes: CSA=ERCC8, CSB=ERCC6, XPG
Mnemonic: Walt Disney on cocaine
Uroporphyrinogen III Synthetase (UPS delivers the baby)
Congenital Erythropoietic Porphyria (CEP)
What is the range of wavelengths known as the Soret band?
What is the GENE mutated in a syndrome characterized by soft, painful, compressible blue cutaneous tumors associated with GI involvmeent and melena?

Name 3 autoantibodies associated with Duhring's Disease.
This autosomal recessively inherited disorder is caused by a mutation in the RECQL2 gene which encodes a DNA helicase.

Name 3 things that can cause pseudoporphyria.
What is the syndrome caused by mutation sin Fibrillin 1 that results in aortic root aneurysms, rupture and dissection as well as mitral valve prolapse?
Which form of porphyria can presnet with porphyrin gallstones in a child?
What is this lesion consisting of red-brown papules which progress to sharply demarcated yellow-brown atrophic, telangiectatic plaques with a violaceous, irregular border? Histology shows palisading granulomas containing degenerating collagen with inflammatory infiltrate containing plasma cells and multinucleated histiocytes.

This autosomal dominantly inherited disorder results from a mutation in COL3A1 encoding procollagen type 3 which results in arterial, bowel and uterine rupture.
Spastic tetraplegia can be seen in which syndrome?
At what wavelength doe plasma fluoresce in Variegate Porphyria?
What are plexiform neurofibromas capable of transforming into in NF1? (either of 2 possible correct answers will be accepted)
Name 3 syndromes associated with the PTEN gene.
What are the genes responsible for a syndrome with hair shaft findings of alternating bright and dark bands?

This disorder is similar to XP with photosensitivity and neurologic degeneration, however in contrast to XP, there is neither premature aging nor skin cancer. Bird-headed facies, "Mickey Mouse" ears and dwarfism are hallmarks of this syndrome.

This autosomal recessively inherited condition results from deficiancy of cystathionine beta synthase.
What is the deficient enzyme in the form of porphyria that presents soon after birth with red urine, erythrodontia, and hypertrichosis?
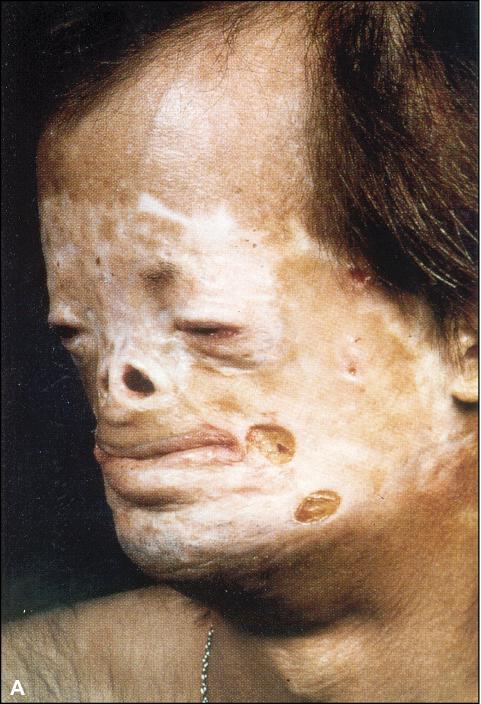
What are these lesions found in this moustached AIDS patient in association with HHV-8?
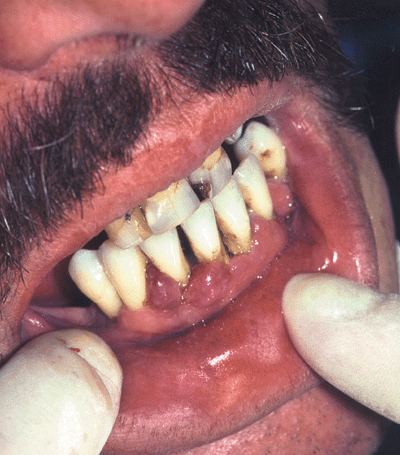
What is the syndrome that can result from mutation in Endoglin?
This syndrome is characterized by osteogenesis imperfecta plus arthrogryposis multiplex.

What is the gene mutated in Bloch-Sulzberger Disease?
What are the individual components of the acronym HAIRAN syndrome?
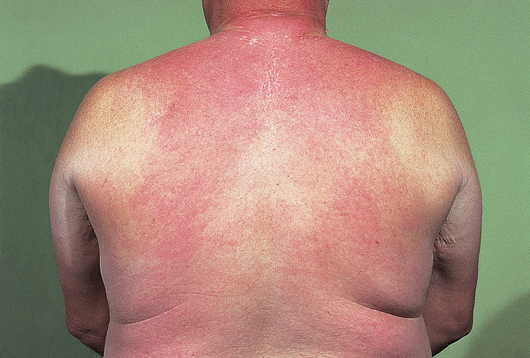
What is the name for the condition which presents as painless, symmetric, woddy "peau d'orange" induration of the upper back and neck in long-standing type 2 diabetic obese males?
What is the name for the condition associated with a positive "prayer sign"

What is this? Hint: It is the most common cutaneous manifestation of diabetes.



| Description | Match: |
What is the syndrome that can result from mutation in Endoglin? | Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia (Osler-Weber-Rendu) Endoglin (ENG) or Activin receptor-like kinase-1 (ACK1, ACVRL1) -> proteins belonging to TGF-beta receptor complex that play a role in forming the vascular system Telangiectasias, epistaxis, melena, AV malformations in liver, lung, CNS |
What are these lesions found in this moustached AIDS patient in association with HHV-8?
| Kaposi's Sarcoma |
Name 3 autoantibodies associated with Duhring's Disease. | aka Dermatitis Herpetiformis: Anti-Gliadin Anti-Tissue Transglutaminase or Anti-Epidermal Transglutaminase Anti-Endomysial |
Name 3 syndromes associated with the PTEN gene. | Cowden's Syndrome Bannayan-Riley-Ruvalcaba Proteus Syndrome |
What is the GENE mutated in a syndrome characterized by soft, painful, compressible blue cutaneous tumors associated with GI involvmeent and melena?
| VMCM1 gene - Blue Rubber Bleb Nevus Syndrome Autosomal dominant or sporadic Cutaneous lesions, GI lesions -> melena Lung, eye and CNS lesions |
What is the gene mutated in Bloch-Sulzberger Disease? | NEMO Incontinential Pigmenti Stages: 1 = Vesicular 2 = Verrucous 3 = Hyperpigmentation 4 = Hypopigmentation |
What are the genes responsible for a syndrome with hair shaft findings of alternating bright and dark bands?
| XPD=ERCC2 or XPB=ERCC3 (DB = Dark Bands) Trichothiodystrophy or PIBIDS or Tay's Syndrome Photosensitivity, Ichthyosis, Brittle hair, Intellectual impairment, Decreased fertility, Short stature Reduced sulfur content in hair Polarosocpy reveals tiger tail banding or trichothiodystrophy. Can also see trichoschisis, pili torti, trichorrhexis nodosa. Photosensitivity but no increased risk of skin cancer.
|
This disorder is similar to XP with photosensitivity and neurologic degeneration, however in contrast to XP, there is neither premature aging nor skin cancer. Bird-headed facies, "Mickey Mouse" ears and dwarfism are hallmarks of this syndrome.
| Cockayne Syndrome Genes: CSA=ERCC8, CSB=ERCC6, XPG Mnemonic: Walt Disney on cocaine |
What are plexiform neurofibromas capable of transforming into in NF1? (either of 2 possible correct answers will be accepted) | Neurofibrosarcoma Malignant Peripheral Nerve Sheath Tumor |
Spastic tetraplegia can be seen in which syndrome? | Sjögren–Larsson syndrome FALDH (Fatty aldehyde dehydrogenase) deficiency (they fall down) --> accumulated fatty alcohol/aldehyde lipids More common in Sweden Triad of congenital ichthyosis, di- or tetraplegia, mental retardation Perifovial glistening white dots (fall down, see stars), grand mall seizures. |
What is the name for the condition which presents as painless, symmetric, woddy "peau d'orange" induration of the upper back and neck in long-standing type 2 diabetic obese males?
| Scleredema Diabeticorum Type 1 = Acute type secondary to strep pyogenes Type 2 = Associated paraproteinemia Type 3 = Type 2 DM |
What are the individual components of the acronym HAIRAN syndrome? | HyperAndrogenism Insulin Resistance Acanthosis Nigricans |
What is the name for the condition associated with a positive "prayer sign"
| Diabetic Limited Joint Mobility = Cheiroarthropathy Tightness and thickening of the skin and periarticular tissue of the fingers with resultant painless loss of joint mobility Physical therapy and tight control of hyperglycemia |
What is this lesion consisting of red-brown papules which progress to sharply demarcated yellow-brown atrophic, telangiectatic plaques with a violaceous, irregular border? Histology shows palisading granulomas containing degenerating collagen with inflammatory infiltrate containing plasma cells and multinucleated histiocytes.
| Necrobiosis Lipoidica Diabeticorum (NLD) Thought to be secondary to nonenzymatic glycosylation of dermal collagen and elastin. Ulcer prevention. No impact of tight glucose control on developing NLD, but diabetics with NLD have higher rate of microvascular complications and limited joint mobility. |
What is this? Hint: It is the most common cutaneous manifestation of diabetes.
| Diabetic Dermopathy or "Shin Spots" or Pigmented Pretibial Papules Bilateral asymptomatic red-brown atrophic macules on the shins No effective treatment. |
What is the syndrome caused by mutation sin Fibrillin 1 that results in aortic root aneurysms, rupture and dissection as well as mitral valve prolapse? | Marfan's Syndrome Striae distensae, abdominal wall hernias, elastosis perforans serpiginosa, upward ectopia lentis, tall stature, hyperextensible joints, pectus excavatum, arachnodactyly, kyphoscoliosis, emphysema, pneumothorax, Gorlin sign |
This autosomal recessively inherited condition results from deficiancy of cystathionine beta synthase. | Homocystinuria Deficient cystathionine beta synthase -> elevated srum homocysteine -> inhibition of collagen cross-linking Arterial and venous thromboses, generalized osteoporosis, mental retardation, downward ectopia lentis. Tx: Avoid methionine and homocysteine. Supplement with cysteine, pyridoxine, folate, B12. |
This autosomal dominantly inherited disorder results from a mutation in COL3A1 encoding procollagen type 3 which results in arterial, bowel and uterine rupture. | Ehlers-Danlos Type IV (Vascular Type) Type 3 collagen abundant in skin, lungs and vasculature. Thin, translucent, easily bruisable skin, thin nose and upper lip. Joint mobility is normal, although atlantoaxial subluxation can occur.
|
This autosomal recessively inherited disorder is caused by a mutation in the RECQL2 gene which encodes a DNA helicase.
| Werner Syndrome (Adult Progeria) Growth arrest at puberty, premature aging/balding/graying, sclerodermoid appearance, poikiloderma, leg ulcers, painful callosities of feet and ankles, and cataracts by age 30 Premature cardiac atherosclerosis accounts for early death Type 2 DM, tumors of uterus, breast, liver and thyroid. |
This syndrome is characterized by osteogenesis imperfecta plus arthrogryposis multiplex.
| Brack Syndrome Arthrogryposis: ("Hooked or curved joints") Multiple joint contractures, muscle weakness, fibrosis |
What is the range of wavelengths known as the Soret band? | 400 - 410 nm |
At what wavelength doe plasma fluoresce in Variegate Porphyria? | 626 nm (diagnostic) |
Name 3 things that can cause pseudoporphyria. | U R Totally Nailed After Last Night's Party, Dude... UVA Renal failure on HD Tetracycline Nalidixic acid (quinolone Abx) Amiodarone Lasix Naproxen/NSAIDs Pyridoxine Dapsone |
What is the deficient enzyme in the form of porphyria that presents soon after birth with red urine, erythrodontia, and hypertrichosis?
| Uroporphyrinogen III Synthetase (UPS delivers the baby) Congenital Erythropoietic Porphyria (CEP) |
Which form of porphyria can presnet with porphyrin gallstones in a child? | Erythropoietic Protoporphyria (EPP) Ferrochelatase deficiency |